- Physics
Quantum Physics
Advance Physics
Quantuam Mechanics, Superconductivity, Electromagnetism
This page explains concepts at college level in the field of quantum mechanics, theory of relativity, superconductivty, Lagrangian method of equation of motion, Solid State Physics, Wave Particle Duality, Diffraction.
Definitions and Formula
- Photons: These are particle-like quanta of electromagnetic radiation which travel at the speed of light c with momentum p and relativistic energy E where p = h/λ and E = hc/λ. Here, h = Plank's constant and λ = wavelength of eletromagnetic radiation.
- de Broglie wavelength: Particle of matter with momentum p could act as a wave with wavelength λ = h/p. the de Broglie wavelength of a particle of matter is very small (as compared to its size) and difficult to measure.
- When the particle is treated as non-relativistic: E = mc2 + EK where EK is the kinetic energy of non-relativistic particle given by EK = p2/2m. Note p = mv and EK = ½mv2 = ½ m×p2/m2 = p2/2m
Classical vs. Quantuam Physics
Reference: Quantum Physics Notes, J D Cresser, Department of Physics, Macquarie University| Classical physics | Quantum Physics |
| Newton’s laws of motion including his law of gravitation, Maxwell’s equations for the electromagnetic field, and the three laws of thermodynamics. | Planck’s theory of black body radiation, Einstein’s theory of relativity and general relativistic theory of gravity, Schroedinger equation, Heisenberg's Uncertainty Relation |
| Objects have a definite position and momentum which we could measure to any degree of accuracy | Apparent certainty and determinism of classical physics, this being replaced by uncertainty and randomness. |
| Everything is pre-determined and there exist a deterministic method to measure the positions and momenta of all the constituent particles of the universe. | Relativistic particles such as photons, de Broglie’s hypothesis of waves particle duality, wave function for particle position, Pauli exclusion principle |
Superconductivity
- The resistivity of a superconductor is practically zero but only below certain temperature known as Critical Temperature, TC.
- When superconducting materials are cooled below their critical temperatures in the presence of a magnetic field, the magnetic flux is expelled from the interior of the superconductor.
- Similarly, superconducting materials lose their superconducting behavior above a certain critical magnetic field, BC which itself is temperature-dependent that is BC = BC(T).
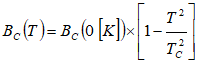
- The value of the critical field limits the maximum [critical] current IC that can be sustained in superconducting materials.
- Critical current in a superconducting wire of radius 'a' is given by IC = 2πBCa/μ0. This is the maximum current the wire can carry at any given temperature and still maintain superconducting features.
Length Contraction
A rod of length L is inclined at angle θ with x-axis [in the moving reference frame] at velocity 0.6c where c is the speed of light in vacuum. Calculate the angle observed in a stationary reference frame.
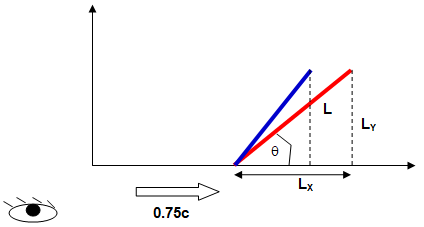
tanθ = LY / LX.
Since rod the moving along X-axis, the length perpendicular to the direction of motion will remain constant as measured my stationary onserver. Thus: LY' = LY.
The contraction in horizontal (X-) component of the length of the rod is given by
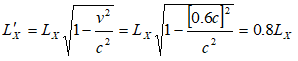
The red line shows rod as seen in moving reference frame and the blue line as observed in stationary reference frame. Thus, angle of inclination in stationary reference frame is given by:
tanθ' = LY / LX' = 1.25 * LY / LX = 1.25tanθ
Superconductivity
A metal behaves as superconductive at 10 [K] and the critical magnetic field at 0 [K] is B0 [A/m]. Calculate the magnetic field at 20 [K].
The critical temperature is TC = 10 [K]. The relative between magnetic field and temperature is given by expression:
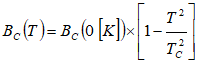
Proper - Improper Time Interval
The ground monitoring team of a spaceship moving at constant speed noted the time difference as per his stop-watch as 9 [s] when the location is shown to be 1.44E109 [m]. Calculate the proper time interval
Note that the definition of proper time interval is "time interval measured in a reference frame where two events occcur at same place". Hence, a person monitoring time in space-ship will measure time at same place and will be the proper time interval, Δt. Thus, the time interval measured by the ground staff is improper time interval, Δt'. We have
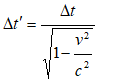
v = 1.44x109 [m] / 9 [s] = 1.8x108 [m/s], Δt' = 9 [s].
Δt = Δt' * 0.8 = 7.2 [s].
Note that a moving clock runs slower than a stationary clock and hence "proper time interval" ≤ "improper time interval".
Relativity and Impulse-Momentum Theorem
Calculate the relativistic speed of a particle of rest mass m0 after time t when a constant force F acts on it. The particle stats with velocity v0 at t = 0.
From Newtons's law: dp/dt = F. Here, the momentum p = m(v) * v where m(v) is mass of the particle at speed v.
Thus:
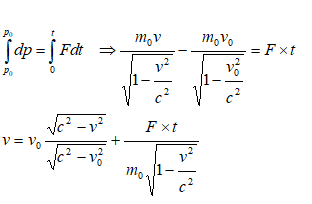
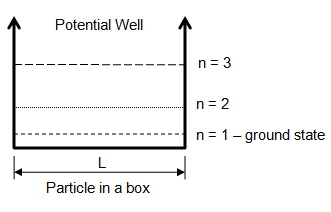
Particle in Box
Calculate the number of bound states for energy (potential) level E = 11h2/[8mL2] where L is the length of the box and h is the Planck's constant.
The potential well for a particle in a box is shown below
The energy level at quantum state 'n' is given by
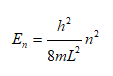
Thus, the equation En < E = 11h2/[8mL2] is satisfied for n = 1, 2 and 3. Hence, number of bound states is 3.
Note that the energy in ground state E1 > 0, whereas the classical physics assigns a value zero to minimum energy level. This excess energy of the ground state (with respect to the classical minimum) is known as zero point energy. Thus, the kinetic energy hence the momentum of a bound particle cannot be reduced to zero. The minimum value of momentum is E1 = p2/2m.
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle
A neutron is moving at velocity 9*107 [m/s]. What is the minimum uncertainty in position of this particle.
The maximum uncertainty in position is size of the box, that is Δx = L. Thus, Δx.Δp ≈ h. Similary, minimum uncertainty in position will correspond to maximum uncertainty in momentum.
Momentum of the neutron particle is given by
p = mn * v = 1.674929 x 10-27 [kg] * 9 x 107 [m/s]
p = 5.165 x 10-19 [kg-m/s] = maximum uncertainty in momentum.
Thus: minimum uncertainty in position, ΔxMIN = h / ΔpMAX
ΔxMIN = 6.626 x 10-34 [kg-m2/s] / 5.165 x 10-19 [kg-m/s] = 1.283 x 10-15 [m].
Probability Distribution: Particle in Box
A particle is located in a box of length L and is assumed to be in ground state. Determine the probability of finding the particle in the region 0.25L to 0.75 L.
The probability distribution function (also known as wave function) is given by 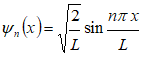
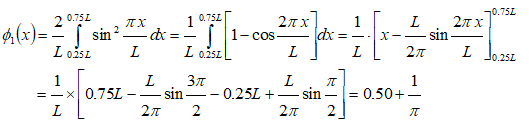
Uncertainty Δx in the position of a particle is given by :
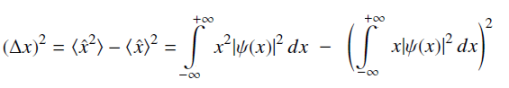
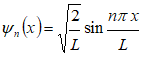
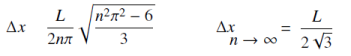
The content on CFDyna.com is being constantly refined and improvised with on-the-job experience, testing, and training. Examples might be simplified to improve insight into the physics and basic understanding. Linked pages, articles, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to reduce errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content.
Template by OS Templates