- College Physics: Wave Optics
Waves and Optics
Waves and Optics
Propagation of Sound and Light Waves
This page explains concepts at college level in the field of wave propagation. The sound and light waves have been clubbed together to highlight lot of similarity in concepts dealing with wave phenomena such as reflection, transmission, interferences and diffraction.
Analogy and similarity between light and sound waves
| Phenomena | Sound Waves | Light Waves | Equation of wave | y = A sinω(t - x/v) | E = E0 sinω(t - x/v) | Speed of wave | v = [γ*RT]0.5 in air, v = [B / ρ]0.5-liquid, v = [Y / ρ]0.5-solid | v = c / μ | Path difference Multiple of wave-length | Δx Physical distance between sources | μ * ΔxVACUUM | Phase difference Multiple of 2π [ = 1 cycle] | δ = Δx * 2π/λ | δ = Δx * 2π/λ | Constructive Interference | Maxima: Δx = n * λ or δ = 2nπ | Bright fringes: Δx = n * λ or δ = 2nπ |
Destructive Interference | Minima: Δx = (2n+1) * λ/2 or δ = (2n + 1)π | Dark fringes: Δx = (2n+1) * λ/2 or δ = (2n + 1)π |
Diffraction and Interference
For example, refer to the interference of waves (including diffraction in case of light). The maxima and minima of sound waves are analogous to the bright and dark fringes and their location can be determined in similar ways.
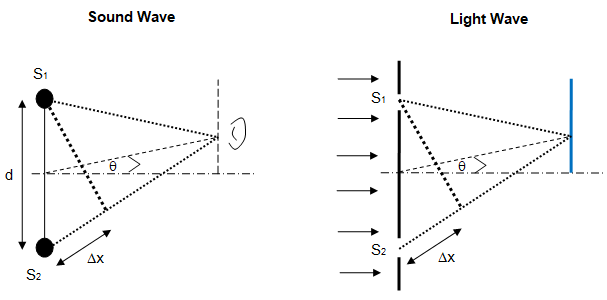
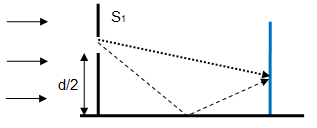
The path difference is given by Δx = d * sinθ ≈ d * tanθ as sinθ ≈ = tanθ for small values of θ.
Note that distance between two consecutive maxima or consecutive minima of sound wave is analogous to the distance between centres of consecutive dark fringes or bright fringes. Note the symmetry of the geometry and wave transmission phenomena. For light wave, the symmetry plane can be also treated as a plane mirror described as follows:
Traveling Wave - String in Tension
The equation of traveling wave on a string is given by y = A * sin[ω(t - x/v)] where v is the velocity of the wave moving from left to right. Following animation has been created to describe the wave motion due to transverse [up-down motion] vibration of each particle of the string. The purpose of this animation to improve the understanding of the phenomena described widely in appropriate textbooks on physics.
Standing Wave - String in Tension
The equation of standing wave on a string is given by y = 2A * sin[nπx/L] * cos(ωt). Following animation has been created to describe the location of nodes and antinodes. The purpose of this animation to improve the understanding of the phenomena described widely in appropriate textbooks on physics.
The content on CFDyna.com is being constantly refined and improvised with on-the-job experience, testing, and training. Examples might be simplified to improve insight into the physics and basic understanding. Linked pages, articles, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to reduce errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content.
Template by OS Templates