- Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Python, Web Scraping: Feedbacks/Queries -

World Wide Web
Programming for the World Wide Web
Table of Contents
Web Technology -|- PHP |-| To-Do Application |*| MySQL |-| Mathematical Equations in HTML |=| PowerBI and Pivot Tables |+| Cursor AI {+} Video editing and streaming using OBS Studio [=] PHP vs. JavaScriptWrite Mathematical Equations in HTML Pages
MathJax is JavaScript display engine for mathematics that works in all browsers. MathML is an XML-based language for describing mathematical notation. AsciiMath is an easy-to-write markup language for mathematics. LaTeX and TeX are another notation system for mathematical equations in HTML pages. Some example scripts for MathML is given below. xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" needs to be added to <math> tag.- <mfrac><mn>1</mn>mn>2</mn></mfrac> =
- <math><msqrt><mo>(</mo><mfrac><mn>A</mn><mn>B</mn></mfrac><mo>)</mo></msqrt></math> =
<mrow> <munderover> <mo>Σ</mo><mrow><mi>n</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mo>+</mo><mn>∞</mn> </mrow></munderover> <mfrac><mn>1</mn><msup><mi>n</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mfrac> </mrow>
: The HTML code is
<mrow>
<munderover><mi>∫</mi><mn>-π</mn><mn>+π</mn></munderover>
<mrow>
<mi>f</mi><mo>(</mo><mi>x</mi><mo>)</mo> <mi>d</mi><mi>x</mi>
</mrow>
</mrow>
Web Technology

| Front-End | Back-end | Full Stack |
| Topic dealing with user interface, what the end user see and interact with | Deals with methods required to create, maintain and provide data needed for Front End | Deals with both Front End and the Back End technologies |
| Mainly programmed in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP | Deals with databases and server-side scripting: PHP, ASPX, SQL, JSON, Angular, ReactJS | In addition to Front End and Back-end, the developers have to deal with servers (ports, networks, web-hosting), data security and database management. MongoDB, NodeJS, PHP, Python |
WAMP stands for Windows, Apache, MySQL, and anyone of PHP, Perl, or Python. LAMP is equivalent set for Linux. WAMP server is a local web server for running the scripting language (PHP, Perl) and this is open source. XAMPP stands for Cross-Platform (X), Apache (A), Maria DB (M), PHP (P), and Perl (P). It is developed by Apache Friends. It includes Apache and MySQL, FileZilla, Mercury, Tomcat, and Maria DB.
- Put files into the destination folder. Default folder is c:/xampp/htdocs, /var/www/html in Linux.
- Type address "http://localhost" in web browser: Opens XAMPP dashboard
- localhost/folderName/index.php: opens personalized page on localhost
- Excertps from Apache2 Ubuntu Default Page: "By default, Ubuntu does not allow access through the web browser to any file apart of those located in /var/www, public_html directories (when enabled) and /usr/share (for web applications). If your site is using a web document root located elsewhere (such as in /srv) you may need to whitelist your document root directory in /etc/apache2/apache2.conf."
Javascript is loosely typed. A variable can contain all data types and a variable can change its data type. Strings created with single or double quotes work the same. Use quotes inside a string, as long as they don't match the quotes surrounding the string. Hoisting is JavaScript's default behavior of moving declarations to the top. In JavaScript, a variable can be declared after it has been used. JavaScript modules allows to break up code into separate file which makes it easier to maintain a code-base. Like Python, with the 'import' statement. 'modules' are imported from external files with the 'import' statement.
document.addEventListener("click", func_name);
function func_name() {
document.getElementById("demo") .innerHTML = "Demo";
}
≡
document. addEventListener("click", function(){
document.getElementById("demo") .innerHTML = "Demo";
}
Select a column from a table on the webpage: No direct method exist though some add-on to web-browsers do exist. Select that table and paste in a text file or a spreadsheet. Use Python with CSV or Pandas modules. Paste the data in MS-Word which allows selecting particular column with mouse drag. For creating a table where columns can be selected, create a nested table. Outer table with only one 'tr' and 'td' tags. Each column as inner 'table' with single 'td' and desired number of 'tr' tags.
The Window object is the top level object in the JavaScript hierarchy and represents a browser window. It is created automatically with every instance of a 'body' or 'frameset' tag.
| DOM Object | Event Handlers Available |
| Checkbox, Radio / Reset / Submit button | onClick |
| Button element | onClick, onMouseOver |
| Hypertext link, Clickable ImageMap | onClick, onMouseOver, onMouseOut |
| Document | onLoad, onUnload, onError |
| Form | onSubmit, onReset |
| Framesets | onBlur, onFocus |
| Selection list | onBlur, onFocus, onChange |
| Image | onLoad, onError, onAbort |
| Text and TextArea element | onBlur, onChange, onFocus, onSelect |
| Window | onLoad, onUnload, onBlur, onFocus |
JavaScript Objects
| Property | Description |
| closed | Returns whether or not a window has been closed |
| defaultStatus | Sets or returns the default text in the statusbar of the window |
| document | Returns the entire HTML document |
| history | a JavaScript object, not an HTML DOM object, part of the Window object and is accessed through the window.history property |
| length | Sets or returns the number of frames in the window |
| location | See Location object |
| name | Sets or returns the name of the window |
| opener | Returns a reference to the window that created the window |
| outerHeight | Sets or returns the outer height of a window |
| outerWidth | Sets or returns the outer width of a window |
| pageXOffset | Sets or returns the X position of the current page in relation to upper left corner of a window's display area |
| pageYOffset | Sets or returns the Y position of the current page in relation to upper left corner of a window's display area |
| parent | Returns the parent window |
| personalb | Sets whether or not the browser's personal bar (or directories bar) should be visible |
| scrollbars | Sets whether or not the scrollbars should be visible |
| self | Returns a reference to the current window |
| status | Sets the text in the status bar of a window |
| statusbar | Sets whether or not the browser's status bar should be visible |
| toolbar | Sets whether or not the browser's tool bar is visible or not |
| top | Returns the topmost ancestor window |
JSON: Javascript Object Notation
A JSON array is equivalent to list in Python and a JSON object is similar to dictionary in Python. Python has standard JSON module where it is parsed using json.loads() method resulting in Python dictionary. A Python dictionary object can be converted into a JSON string using the json.dump() method.PHP is white space insensitive, case-sensitive, statements are terminated by semicolons, variables start with $, constants created by define() function e.g. define("pi", 3.1416), {...} create blocks - a sequence of multiple statements (concatenation of statements). Unlike with variables, constant does not need to start with a $. Logical operators uses both ('and' &&), ('or' '||'). Loop uses parentheses for logical argument: if () ... elseif () ... else ... Single-line comments: # or //. */ .... /* is used for multiline comments. PHP Magic constants: __LINE__, __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __CLASS__, __METHOD__, $_POST (is a PHP super global variable which is used to collect form data after submitting an HTML form with method = "post").
The double arrow operator '=>' is used as an access mechanism for arrays. => is used in associative array key/value pairs for assignment that is => is used to assign values to the keys of an array. PHP is a server side language: nothing inside the "<?php ... ?>;" blocks will ever be visible in the browser. User names and passwords are required to connect to various databases. They are secure so long they remain inside PHP tags. include_once( "../../sub-folder-x/connect_mysqli.php"); can be used to avoid keeping connect_mysqli.php file into sub-folders along with index.php file.
PHP-enabled web pages are treated just like regular HTML pages and they can be created / edited the same way as normally done for regular HTML pages. Codes can jump in and out of PHP mode even in the middle of a PHP block while the logical flow of the script remains intact. This is similar to how image and equations can be put inline with text in a MS-Word file or how PERL scripts are used in CCL (CFX Command Language). PHP code can be embedded in the middle of an HTML opening tag. Instead of using PHP echo statement, one can jump out of PHP mode and just sent straight HTML. The PHP parser doesn't care that it is in the middle of an opening tag, and doesn't require that it (HTML tag) be closed. It also allows the cases where the closing ?> tag is at the end of the HTML opening tag, just before > of HTML tag.
<?php if ($expression == true): ?> Show if the expression is true. <?php else: ?> Otherwise show this. <?php endif; ?>Similarly, following code shall print "Hello, there!" 4 times.
<?php for ($i = 0; $i < 5; ++$i): ?> Hello, there! <?php endfor; ?>Tag "<?=" is shorthand for "<? php echo". The super global variable $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] returns the filename of the currently executing script. The htmlspecialchars() function converts special characters like < and > to '<' and '>' which prevents Cross-Site Scripting attacks. Use stripslashes() and preg_match('/^[a-zA-Z0-9]+$/', $username) functions for additional sanitization of user inputs. Regular expression '/^[a-zA-Z0-9_.]+$/' can be used to allow underscore and dot. $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] exploits can be avoided by using the htmlspecialchars() function. if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") { .. } checks the method used to submit a form. Prepared Statements and Bound Parameters are useful against SQL injections.
Error Reporting and Debugging: Quite often while running a PHP script, one gets a blank screen, no error message but just the empty screen. The reason might be syntax error, failed function call, or something else. One need to turn on the error display options. Use "sudo find /etc -name php.ini -type f" to find the location of php.ini file (something like /etc/php/7.4/apache2/php.ini) and set "display_errors = On" in the file. The location (path) of php.ini file can also be looked into the output generated through phpinfo(); function. php.ini: update line "mysqli.default_user =" to mysqli.default_user = "root". Some programs may access fields such as $username = ini_get("mysql.default_user"); $passwd = ini_get("mysql.default_password");
Depending on which files user developer has access to, it may be needed to configure display_errors in .htaccess or PHP.ini file. Many hosting providers do not allow modification to PHP.ini file. In production version of codes, error messages must not be shown to the end users, yet information must be recorded for tracing purposes. The common way to record error messages in production environment is to store it in log files.
When working with PHP and AJAX calls, errors is difficult to track as they do not get displayed in the browser rather they are returned to the AJAX request.The @ symbol, when placed before an expression, acts as an error control operator. When used with 'include' or 'require' statements, it suppresses error messages that would get generated if the included file cannot be found or if there is an issue during its inclusion.
"Notice: Undefined index" occurs when attempting to access an array key that does not exist within the array. This is a common warning, not a fatal error, but it indicates a potential issue in the code where an expected array key is missing. Use error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE); to suppress the warning (notice) messages.debug_backtrace() generates a PHP backtrace, Returns an array of associative arrays. When an error occurs, debug_backtrace() can identify the exact function or method call that triggered it. debug_print_backtrace() prints a PHP backtrace. It prints the function calls, included/required files and eval()ed stuff. No value is returned.
User Defined Functions in PHP:
A function is defined using the function keyword, a name, a list of parameters (which might be empty) separated by commas (,) enclosed in parentheses, followed by the body of the function enclosed in curly braces. Functions need not be defined before they are referenced, except when a function is conditionally defined. By default, function arguments are passed by value (so that if the value of the argument within the function is changed, it does not get changed outside of the function).<?php
$x = 5.0;
echo nl2br("$x \n"); // Output: 5
function sqr($x) {
$x = $x * $x;
return $x;
}
echo nl2br("$x \n"); // Output: 5
echo nl2br(sqr($x) \n"); // Output: 25
?>To have an argument to a function passed by reference, prepend an ampersand (&) to the parameter name in the function definition.
JavaScript
- Global Functions: eval(), isNaN(), parseInt(), parseFloat()
- String Methods: length, toUpperCase(), toLowerCase(), substring(), indexOf(), replace()
- Array Methods: length, push(), pop(), shift(), unshift(), splice(), slice(), forEach(), map(), filter(), reduce()
- Number Methods: toFixed(), toPrecision()
- Date and Time: Date() object and its methods
- Math Object: Math.abs(), Math.round(), Math.random(), Math.floor(), Math.ceil()
- Asynchronous Operations: setTimeout(), setInterval()
PHP vs. JavaScript
| Feature | PHP | JavaScript |
| String Manipulation | strlen(), str_replace(), explode(), implode() | length, replace(), split(), join() |
| Array Handling | array_push(), array_pop(), array_keys(), array_values() | push(), pop(), keys(), values() |
| Type Conversion | (int), (float), (string), intval(), floatval() | parseInt(), parseFloat(), String(), Number() |
| Input/Output | echo, print(), file_get_contents(), file_put_contents() | console.log(), alert(), fetch() (for network I/O) |
| Date & Time | date(), strtotime(), time() | Date object methods: getFullYear(), getMonth(), getTime() |
| Category | PHP | JavaScript | Example Code Snippet |
| Output | echo, print | console.log() | PHP: echo "Hello"; JS: console.log("Hello"); |
| String Length | strlen() | .length property | PHP: strlen("Hello") JS: "Hello".length |
| Substring | substr() | substring() / slice() | PHP: substr("Hello", 1, 3) JS: "Hello".slice(1, 4) |
| String Replace | str_replace() | replace() | PHP: str_replace("a", "b", "cat") JS: "cat".replace("a", "b") |
| Find in String | strpos() | indexOf() | PHP: strpos("Hello", "e") JS: "Hello".indexOf("e") |
| Array Length | count() | .length property | PHP: count([1, 2, 3]) JS: [1, 2, 3].length |
| Array Merge | array_merge() | concat() | PHP: array_merge([1], [2]) JS: [1].concat([2]) |
| Check if in Array | in_array() | includes() | PHP: in_array(2, [1, 2, 3]) JS: [1, 2, 3].includes(2) |
| Loop - For Each | foreach loop | forEach() method | PHP: foreach($arr as $val){} JS: [1,2,3].forEach(v => {}) |
| JSON Encode | json_encode() | JSON.stringify() | PHP: json_encode(["a" => 1]) JS: JSON.stringify({a: 1}) |
| JSON Decode | json_decode() | JSON.parse() | PHP: json_decode('{"a":1}') JS: JSON.parse('{"a":1}') |
| Date/Time Now | date("Y-m-d H:i:s") | new Date() | PHP: date("Y-m-d H:i:s") JS: new Date().toISOString() |
| Math Round | round() | Math.round() | PHP: round(2.5) JS: Math.round(2.5) |
| Random Number | rand(min, max) | Math.random() + scaling | PHP: rand(1, 10) JS: Math.floor(Math.random()*10+1) |
| Type Check | is_array(), is_string(), etc. | typeof, Array.isArray() | PHP: is_array($x) JS: Array.isArray(x) |
| File Read | file_get_contents() | fetch() / FileReader API (async) | PHP: file_get_contents("file.txt") JS: fetch('file.txt') |
| Variable Dump | var_dump(), print_r() | console.log() | PHP: var_dump($x) JS: console.log(x) |
| Set Timeout | Not built-in; use sleep() | setTimeout() | PHP: sleep(2) JS: setTimeout(() => {}, 2000) |
| Define Constant | define() | const keyword | PHP: define("PI", 3.14) JS: const PI = 3.14 |
| Function Declare | function myFunc() {} | function myFunc() {} or arrow function | PHP: function greet() {} JS: const greet = () => {} |
Both MySQLi (the "i" stands for improved) and PDO (PHP Data objects) have their advantages: PDO will work on many (almost all) different database systems, whereas MySQLi will only work with MySQL databases. So, switching project to use another database is easier with PDO. One only have to change the connection string and a few queries. With MySQLi, the entire code will need to be rewritten - queries included. Both are object-oriented, but MySQLi also offers a procedural API. PDO has an exception class to handle any problems that may occur in database queries.
MySQLi Object-Oriented: | MySQLi Procedural
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<?php
$srv = "localhost"; | <- same
$usr = "username"; | <- same
$pwd = "password"; | <- same
// Create connection
$con = new mysqli($srv, $usr, $pwd); | $con=mysqli_connect($srv, $usr, $pwd);
// Check connection
if ($con->connect_error) { | if (!$con) {
die("Fail: ".$con->connect_error); | die("Fail: ".mysqli_connect_error());
} | }
$con->close(); | mysqli_close($con);
?>
Strings (text can contain HTML markup) are surrounded by (single or double) quotes, but with double quotes variables can be inserted to the string directly and using single quotes variables have to be inserted using the '.' dot operator. For example:
$str1 = "AI ML"; $str2 = "cfdyna.com"; echo '<p>Sample codes in ' . $str1 . 'at' . $str2.'<p>'; or echo "<p>Sample codes in $str1 at $str2.<p>";Variables can be defined in a file say named as 'common_vars.ph'. Then, this file can be included in any other file and variables defined can be used in the calling file within <?php ... > tags. For example, creation of a form can be parametrized as <input type="text" name="<?php echo $tag_username;?>" value="<?php echo $value_username;?>">
strval(string): Get the string value of a variable - this is useful function to convert arguments of a function into string before adding the information into database. Thus, $sql = "SELECT * FROM tasks WHERE username = '".$username."'"; can be simplified to combination of following two statements: $username = strval($username); and $sql = "SELECT * FROM tasks WHERE username = '$username'";
Handling Passwords: password_verify — Verifies that a password matches a hash e.g. $does_pw_match = password_verify( $user_pass, $stored_pass ); $stored_pass = password_hash( $user_pass, PASSWORD_DEFAULT ); where password_hash( ) creates a new password hash using a strong one-way hashing algorithm PASSWORD_DEFAULT.
MySQL: COMMENTS are from a '-- ' to the end of the line. The double dash-comment style requires at least white space or control character (space, tab, newline...) after the second dash. From a '#' to the end of the line, C-style comment /* ... */ can span multiple lines. You use this comment style to document a block of SQL code. MySQL does not support nested comments. Log-in to MySQL: mysql -u root -p and then enter the password, type 'quit' on mysql prompt to close the session.
- Convention: any entry containing an underscore is user input
- String and date values in MySQL used with either single or double quotes, but single quotes are more standard. INT signifies that the column holds integers (numeric values with no fractional part). UNSIGNED disallows negative values. NOT NULL requires that the column value must be filled in. This prevents members from being created without an ID number. AUTO_INCREMENT is a special attribute in MySQL. It indicates that the column holds sequence numbers. The PRIMARY KEY clause indicates that the the column is indexed to allow fast lookups. It also sets up the constraint that each value in that column must be unique. An ENUM (enumeration) column which means it can take only one of the values listed in the column specification. Storage engine clause, if present, names the storage engine that MySQL should use for creating the table.
- MySQL expects dates to be written in 'CCYY-MM-DD' format
- Check mysql version: SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "%version%";
- Get installation directory: which mysql on Linux prompt. To clear screen: system clear; \! is used to execute system shell commands and hence \!clear; works too. \! pwd; can be used to get working directory.
- Create a database named db_name: create database if not exists db_name;
- Check what the default database is: select database(); To add a database to current project: use db_name; The keyword 'none' shall appear in the command prompt (MariaDB [(none)]>) if no database is selected.
- Create database named db_name with commands input from SourceFile.sql: mysql db_name < SourceFile.sql
- Login and activate database named 'db_name': mysql -h host_name -p -u user_name db_name
- List all the database names being managed by MySQL server to which the current user is logged in: show databases;
- Get list of users: SELECT user FROM mysql.users;
- Create a new user: CREATE USER user_name IDENTIFIED BY PASSWORD user_passwd; Note that the user_name should be enclosed in quotes. User name should be specified at user_name@host_name such as 'abc'@'localhost'.
- Show privileges granted to a user: SHOW GRANTS FOR 'user_name'@'host_name';
- flush privileges; Required to inform MySQL to reload the privilege after the change is made.
- Add specified privileges to a user: grant select, insert, update, delete on *.* to ‘user_name’@’host_name’;
- Add a user name on a host: INSERT INTO table_name (Host, User, Password) values('host_name', 'user_name', PASSWORD('user_passwd’));
- Change password for a user: SET PASSWORD FOR 'user_name'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('new_password'); FLUSH PRIVILEGES; For newer versions: ALTER USER 'user_name' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password';
- Remove a user: drop user 'user_name'; Note that the user name must be in single quotes. delete from user where user='user_name’ and host='host_name';
- Create table named tab_name with column headers identified by column_designation: CREATE TABLE tab_name (column_designation);
- List all tables in currently active database: SHOW tables;
- Display information only for columns that match a given pattern %name where ‘%’ is a wildcard character: show columns from tab_name like ‘%name’;
- Show whole content of a table: SELECT * FROM tab_name;
- Add records into a table, for all the columns: INSERT INTO tab_name VALUES (value1, value2 ...);
- Start the auto_increment other than 1, 37001 in this example: ALTER TABLE tab_name auto_increment = 37001;
- load data infile 'c:\MySQL\tab_input.csv' replace into table tab_name fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' field_names;
- Check structure of a table: DESCRIBE tab_name; or SHOW COLUMNS FROM tab_name; or show fields from tab_name
- Insert several rows into a table with a single INSERT statement by specifying multiple value lists: INSERT INTO tab_name VALUES (...), (...); Parentheses enclose the set of column values for each row. INSERT INTO tab_name (col_name1, col_name2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...);
- Execute text file containing SQL queries: source queries_list.sql;
- Load data from a CSV file into a table: load data infile input_data.csv replace into table tab_name fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' Field_1, Field_2, Field_3 ignore 1 lines; Note that in the example, only 3 fields are being updated. Ignore option is used to ignore few lines such as header of the input file.
- load data local infile 'input_data.txt' into table tab_name; It assumes that input_data.txt is located in the current directory on the client host. By default, the LOAD DATA statement assumes that column values are separated by tabs and that lines end with newlines. It also assumes that the values are present in the order that columns are stored in the table.
- Change attributes of field 'id' in a table: ALTER TABLE tab_name CHANGE `id` `id` SMALLINT( 5 ) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT;
- Update a new record into the table emp_info: UPDATE INTO emp_info (first_name, last_name) value(‘ABC’, ‘LMN’);
- Update additional records to the entry updated in previous step: update emp_info set PAN = ‘ABCAB3461N’ where last_name=’LMN’ and first_name=’ABC’;
- Add column after (to the right of) an existing column: ALTER TABLE tab_name ADD COLUMN col_name VARCHAR(32) AFTER existing_column;
- Change a column name: alter table tab_name change old_col_name new_col_name varchar (32);
- Make a unique column to avoid duplicity: alter table tab_name add unique col_name;
- Delete unique column from table: alter table tab_name drop index col_name;
- Wipe out data completely from a table: delete from tab_name;
- Rename a table: rename old_tab_name to new_tab_name;
- Delete a table completely: drop table tab_name;
- delete from tab_name where "Query String"; Deletes specific records matching query string. For example, delete from tab_emp_info where first_name=’ABC’ and last_name = ‘LMN’;
- Delete a database: drop db_name;
Option-1: read files which contains SQL queries
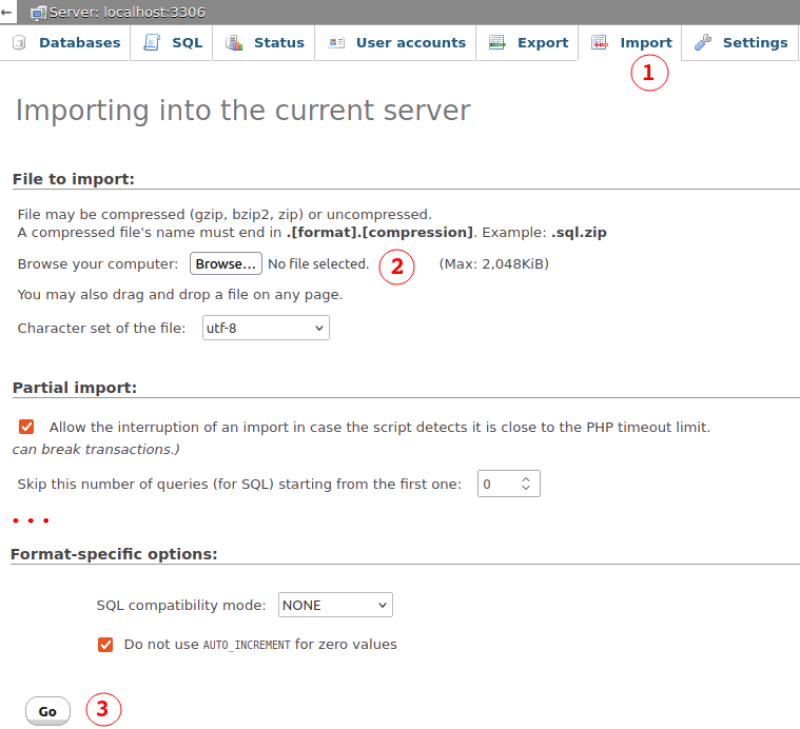
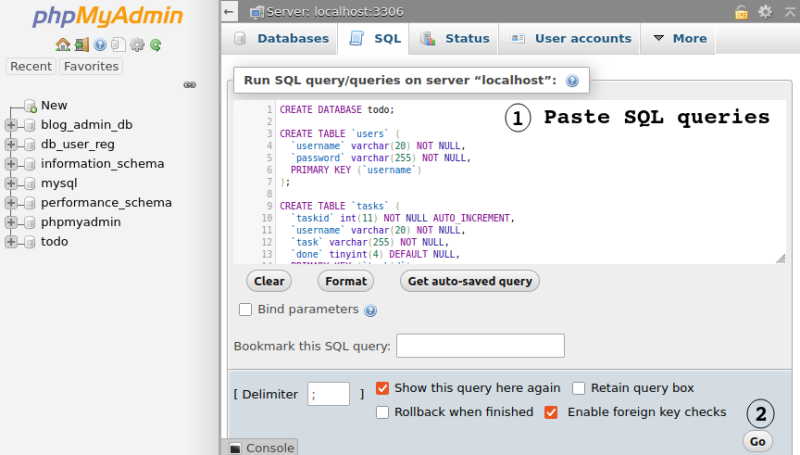
Option-2: Copy-paste SQL queries
Commons Errors:
Failed to connect to MySQL: Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES), Failed to connect to MySQL: Unknown database 'web_admin_db'
Catching error in SQL Queries:
$sql_cmd = "INSERT INTO tbl_members(`username`, `email`, `password`) VALUES(?,?,?)";
$stmt = $conn -> prepare($sql_cmd);
if ($stmt === False) {
die('Error preparing SQL statement: ' . $conn->connect_error);
}
Steps to create a responsive page with LAMP: assuming LAMP is successfully configured. Default path for local server in Ubuntu: /var/www/htm. The URL to phpMyAdmin on local machine is "localhost/phpmyadmin". Check if /etc/phpmyadmin file is available. "sudo service apache2 restart" will result in error if server not installed. Use sudo apt-get install phpmyadmin to install from command line.
Installing phpMyAdmin may give error message "Connect failed: Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: NO)" and shall ask to chose one of the 4 options. Chose 'ignore' to continue installation (use 'tab' key to select <ok>). Now loading "localhost/phpmyadmin" shall result in page looking like this: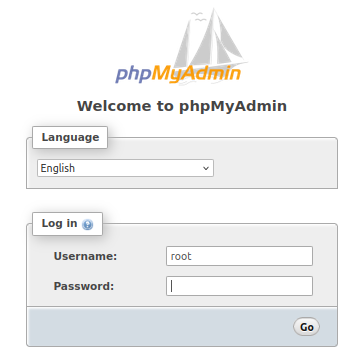
Likely errors: mysqli_real_connect(): (HY000/1045): Access denied for user 'phpmyadmin'@'localhost' (using password: YES). Solution: get password from /etc/phpmyadmin/config-db.php >> run SQL Query: CREATE USER 'phpmyadmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'passwd'; >> Run another query: "flush privileges;" to apply the changes. Another error: 'The phpMyAdmin configuration storage is not completely configured, some extended features have been deactivated. Find out why. Or alternately go to 'Operations' tab of any database to set it up there." Get file "resources/sql/create_tables.sql" from github repository of phpmyadmin and run the SQL query from this file. Alternatively, under phpMyAdmin dashboard: go to "User Accounts", select 'phpmyadmin' under "User name" and then "Edit privileges".
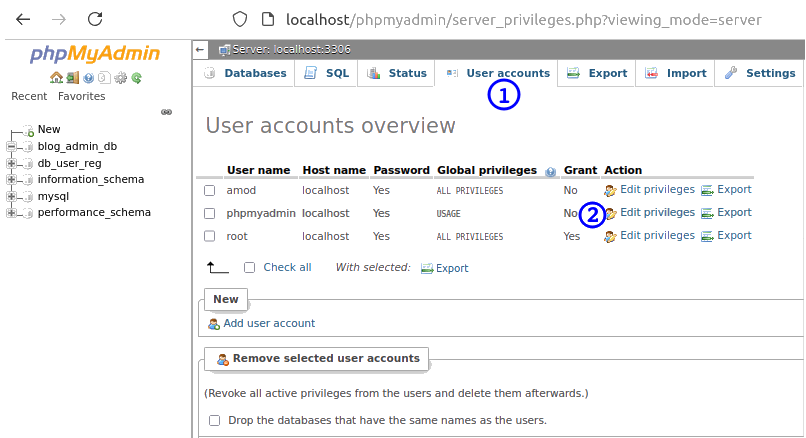
Files to configure MySQL
- /etc/mysql/mariadb.cnf: to set global defaults
- /etc/mysql/conf.d/*.cnf: to set global options
- /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/*.cnf: to set MariaDB-only options
- ~/.my.cnf: to set user-specific options.
Now actual database and PHP stuff:
Step-1:
Define the folder structure named as jas (JavaScript), css, dab (database), adm (administrative stuff), img (images only), vid (videos only), ico (icons only), doc (PDF, DOC and other files), sql, api, lib, tpa (third party)... and create a Readme.txt file to describe what these folders contain and/or are expected to contain. Following is an example for user registration: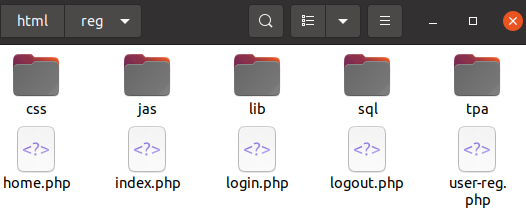
Step-2:
Log-in to mysql terminal and create database(s) and table(s) using command and method described above. A database db_user_reg was created from command prompt. A text file contain SQL commands can be used to create table(s). Alternatively, phpMyAdmin dashboard can also be used to create and view the table.
Step-3:
Create login and user registration form using standard HTML and CSS features. A good starting point is "github.com/keerti1924/PHP-MYSQL-User-Login-System" which seems to work without any modifications. A modified version can be downloaded from here. Minor updates such as trimming user inputs, ensuring alpha-numeric user names and e-mail addresses, password length between 8 to 16 characters with at least 1 special character, prepare() and bind_param() used for database updates. A simple forgot password page has been added. There is no check if user has entered a real e-mail address or not, click on 'eye' icon shows password only for one input field.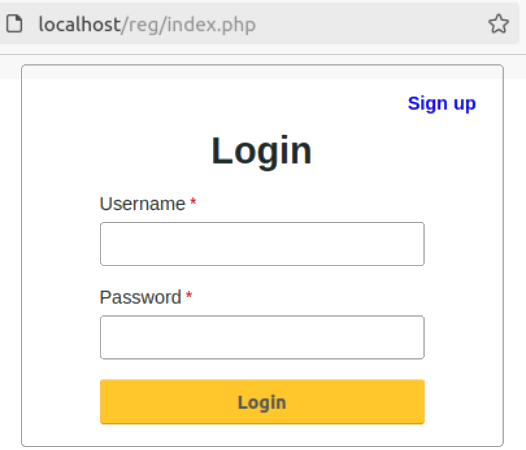
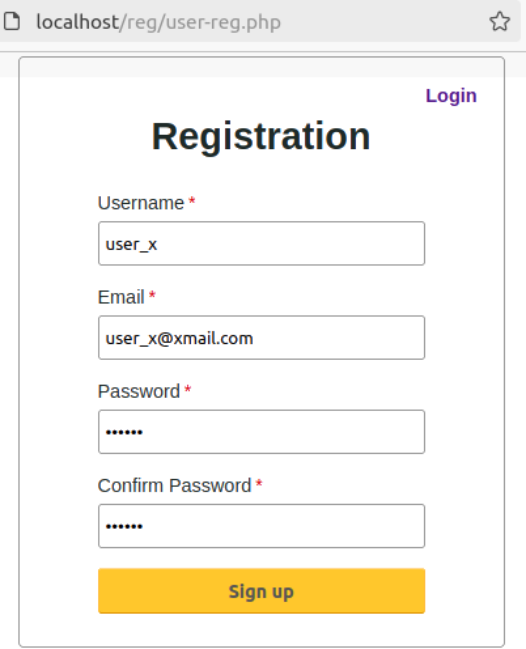
Step-4:
Create the landing page after successful login or new user registration.Security issues: 'Form' resubmission using refresh (F5) or "Go back one page" logs-in user and/or repeats last operation such as adding same information into the database again.
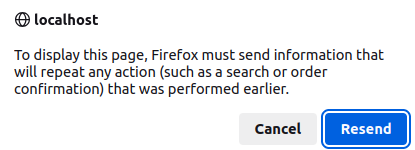
<?php
header("Cache-Control: no-cache, must-revalidate"); // HTTP/1.1
header("Expires: Sat, 01 Jan 2020 05:00:00 GMT"); // Date in the past
?>
Some guidelines: create separate SQL command files for create and alter operations. Do not put JavaScript code inside the body - store these scripts in separate files. Follow a convention for naming: tab_ or tbl_ and db_ for table names and database names, for example db_user_reg. Add version and last update at the beginning of each file.
To-Do Application: Another example is taken from github.com/dhiraj-01/Todo-PHP to create a "ToDo List". Some modifications have been done to disable caching and prevent form resubmission on page refresh. This is a very simple set of codes for learning and demonstration. The updated version can be downloaded from here.
The folder structure of modified version is as shown below.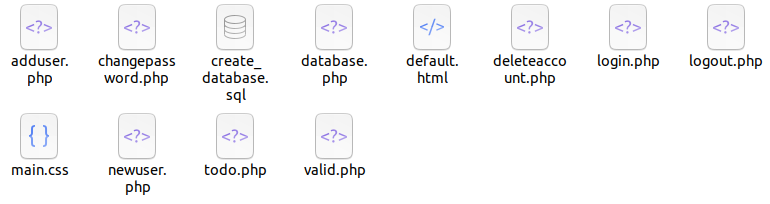
signup.php
|
*-- includes default.html and lib/database.php
*-- checks if user is logged-in and sets location to todo.php
*-- prints (echo) error message above the form section
*-- generates sign-up form and calls lib/adduser.php after Submit
| |
| *--- calls createCAPTCH() function to generate CAPTCHA
| |
| *--- adduser.php
| |
| *-- includes database.php (collection of all functions)
| *-- collects inputs: username, password, secret key and CAPTCHA
| *-- call createUser() function
| |
| *-- validates username, password and secret key
| |
| * alpha-numeric usernames
| * password with special character, length between 6 to 10
| * secret key: up to 6 numeric characters
| *--- if criteria met, adds user
| *--- if not, directs to signup.php which prints error message
login.php
|
*-- form submission directs to lib/valid_inputs.php
*-- function haveValidInputs() defined in database.php is used to check inputs
*-- checks if specified user name exist
`-- checks specified password with stored password using password_verify()
|
todo.php
|
*-- called after successful login
| |
| *-- option to change password with secret key used during sign-up
| *-- generates single line form to get to-do text
| *-- retrieves existing to-do string using getTodoItems() function
| *-- adds new to-do string using addTodoItem() function
|
`*--lib/forgot_password.php
|
*-- form submission directs to lib/resetPassword.php
`*- resetPassword() function from database.php is used to update password
|
*-- checks for valid username, secret key and new password
*-- re-directs to signup.php is invalid inputs are provided.
Further improvement can be to add counter for 3 wrong attempts to log-in, send OTP to specified e-mail to reset password or secret pin, retain valid inputs when page is refreshed for invalid inputs, better background... As one can deduct, the code structure gets complicated even with simplest possible web page having server-side scripts.
Refer the example of Responsive Blog here from 'code-projects.org' which contains 140 different .php files (folder tree contains 41 directories, 266 files). A complete description of code structure with the inter-dependence of files and folders cannot be covered in few pages of a note book. The readme.txt file in this zip folder explains basic steps to make the repository working. The attached ZIP file is working on Ubuntu LTS 20.04, PHP version 7.4, Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu), phpMyAdmin 4.9.5deb2 and server version 10.3.39-MariaDB. Readme.txt file has been updated based on experience gained to make the code working.
Server Administration, Data Security and Hacking: Social Media Hunting, Data Theft, Tracking Personal Information
There are 52 characters (including lower and upper cases), 10 digits and 32 special characters on computer keyboard. If one does not allow to have password starting with special character and minimum size of password is set to be 8 characters, just for passwords having 8 characters, 62 x 947 = 4020 trillion combinations are possible. Note that passwords can be any size higher than 8 characters but usually it would limited to 12 ~ 16 characters as users need to remember them.Most Basic Web Security Tips: [1] Prevent access of folder through browser such as https://www.abc.com/pqr/ - Use .htaccess file, [2] whois: This prints personal details of the website owner if privacy protection is not enabled or purchased from domain name provider, [3] wget or libwww: this Linux command can download entire content of a website: Change HTTP User Agent - RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} wget.* [NC], [4] Prevent access to crawlers: use Robot.txt file, [5] Prevent an htaccess file from being viewed: add following line:
<Files .htaccess> order allow,deny deny from all </Files>
Browser Automation and Server Side Scripting:
Selenium, Pupeteer, Playwright, Headless browsers. Server side scripting: jQuery (JavaScript Framework), PHP, Ruby, Django (server side framework, free, open source and written in Python), Node.js (free, open source tool to run JavaScript outside the web browser), AngularJS (to extend HTML with new attributes). MongoDB is a document database which stores data in a type of JSON format called BSON.jQuery
'$' is alias for 'jQuery' and '$()' is shorthand for "$(document).ready()". Code included inside $(window).load(function() { ... }) will run once the entire page (images and iframes), not when just the DOM is ready.PowerBI and Pivot Tables
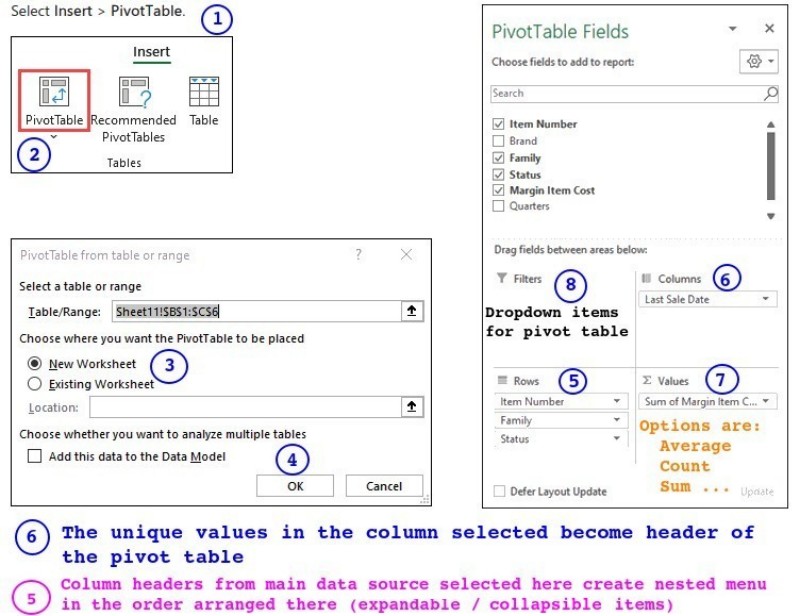
Excerpt from Microsoft website about PowerBI: Find insights in your data and share rich analytics reports. Explore your reports to find and generate the quick insights you need for better business decisions. Collaborate on reports with colleagues, then easily share reports and insights in workspaces, on the web, in apps, via Microsoft Teams.How to Create a Pivot Table
Cursor AI
Tag line on official website: "The AI Code Editor". More from website: "Cursor lets you write code using instructions. Update entire classes or functions with a simple prompt. Cursor's agent mode completes tasks end to end. It does this quickly, while keeping programmers in the loop. We support all frontier coding models, including Claude Sonnet 4, OpenAI o3-pro, OpenAI GPT-4.1, Gemini 2.5 Pro, Claude Opus 4, and more."Thus, Cursor AI is a code editor that uses artificial intelligence models to help code writers with coding tasks such as code generation, smart rewrites, codebase queries and end-to-end task completion.

OBS Studio FAQ
OBS stands for Open Broadcaster Software - an open source software to record screen and stream live on platforms like YouTube. In this section some of the tips and tricks are summarized which has been observed and received from other videos and demos. MB stands for Mouse Button. Unlike other programs, OBS does not have option to Save File... Instead is uses Profile for the same purpose. Excerpts from user guide: "A Profile saves most a solid chunk of OBS Studio settings, primarily related to outputs. Using Profiles lets you to switch between different saved settings quickly depending on the stream or recording a user is working on. Scene Collections save all Scenes and Sources that have been added to it. Similar to Profiles for output settings, you can store multiple different collections of saved Scenes and Sources. Then, you can swap between different collections for different situations. Scene Collections do not store output settings."
Studio Mode: It helps to queue-up the scenes (by creating new scenes or selecting from existing ones) and preview while streaming or recoding.
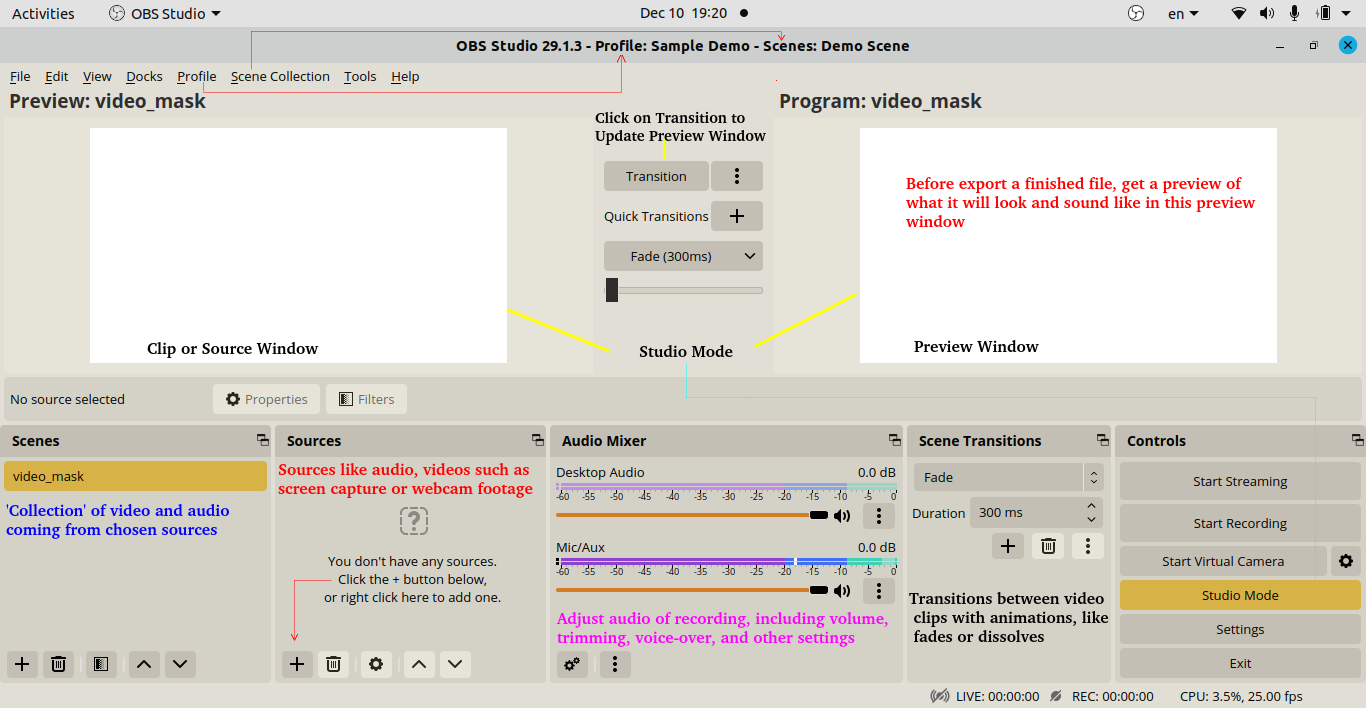
- Alt + Left MB: crop any source object such as image, web camera...
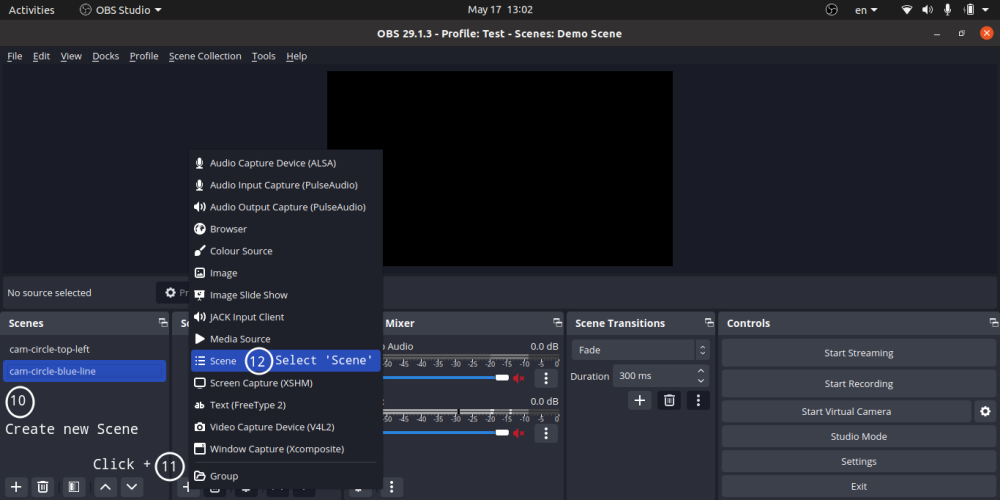
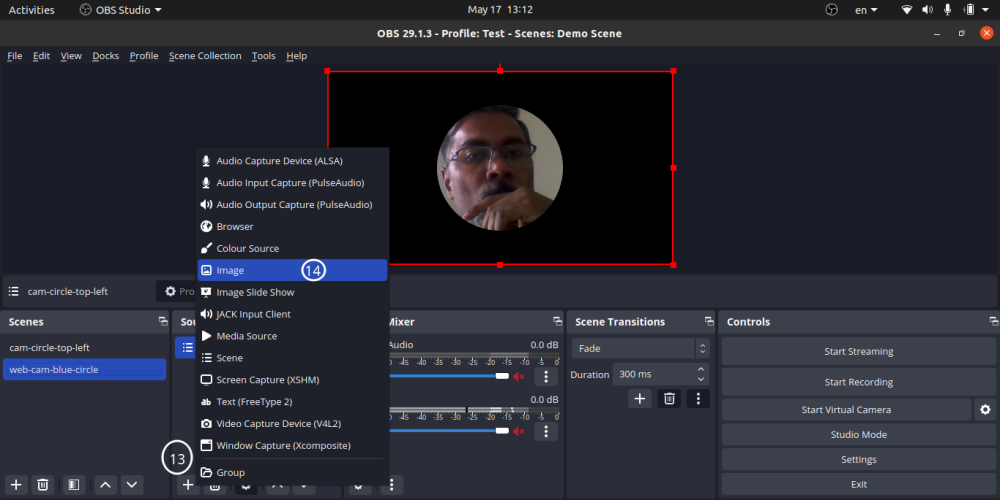
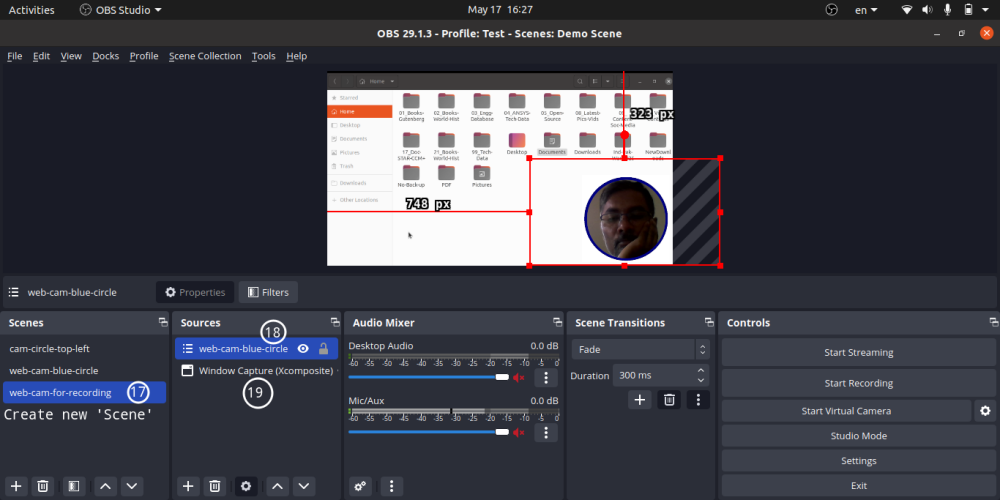
- Video overlap: add any scene to main scene - for example to overlay video scene (Video Capture Device with mask added to it)
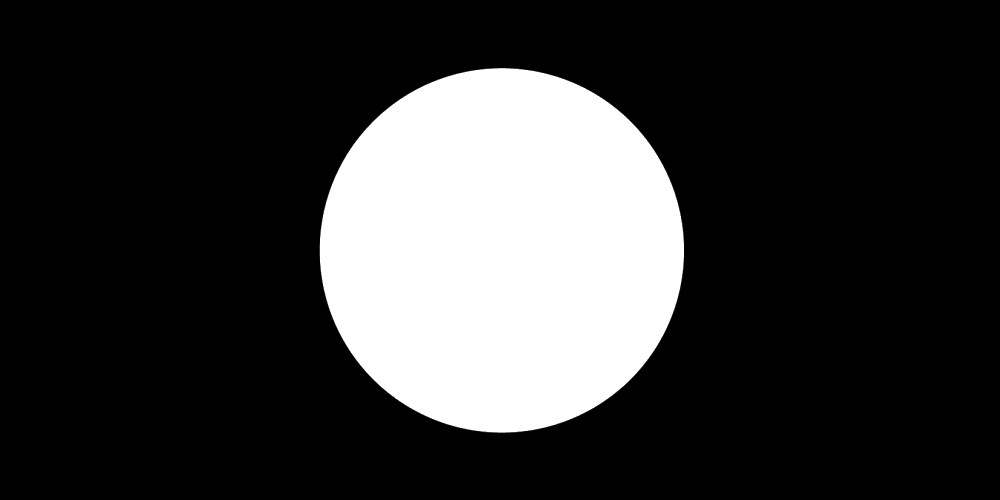
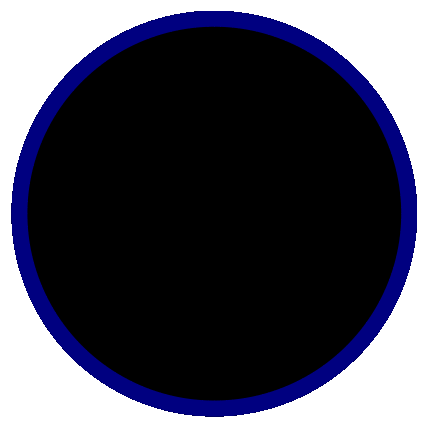
- Like any other program, white portion of an image acts as transparent section of the mask.
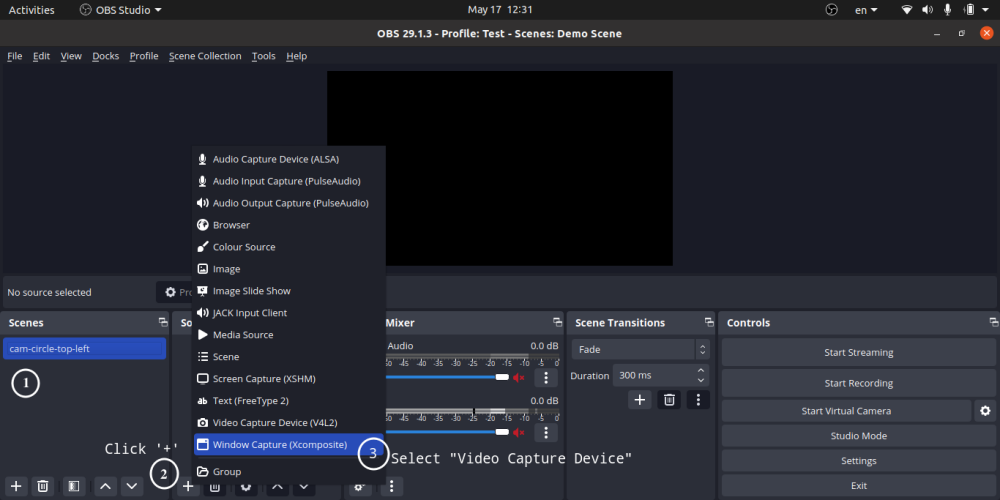
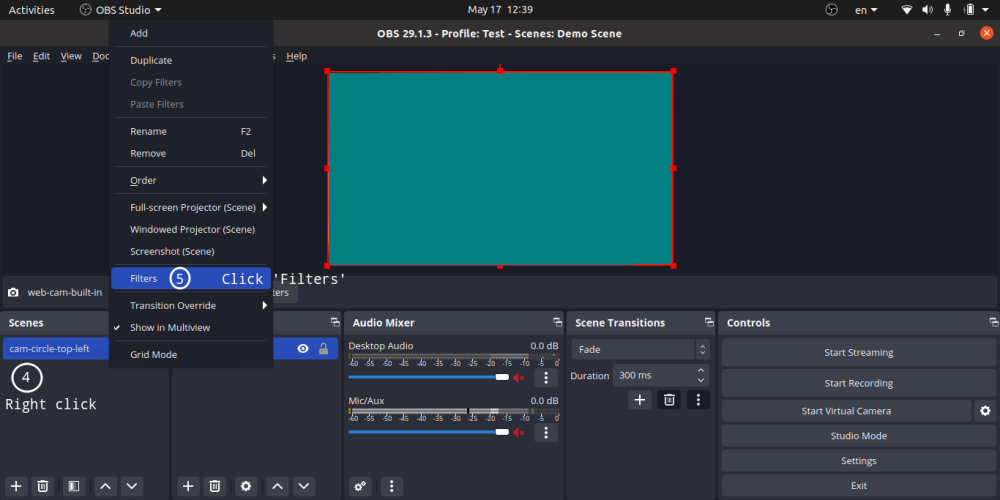
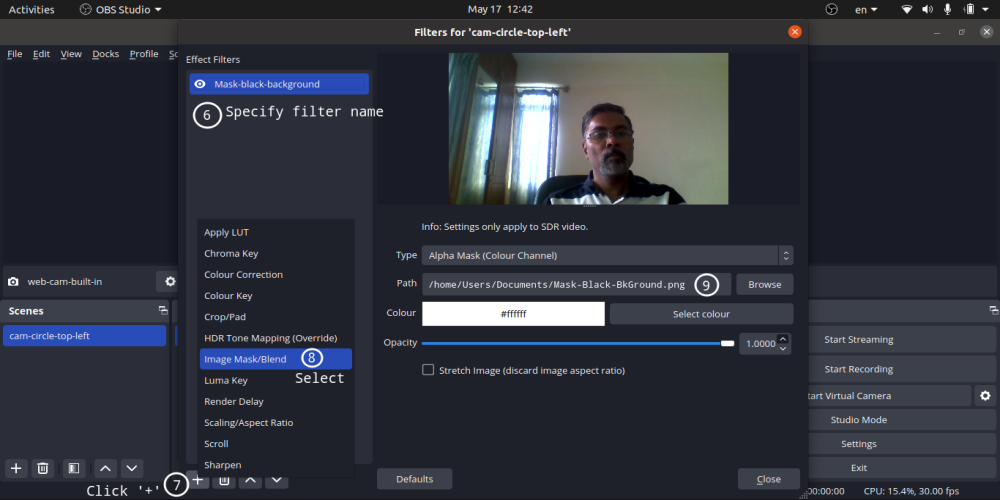
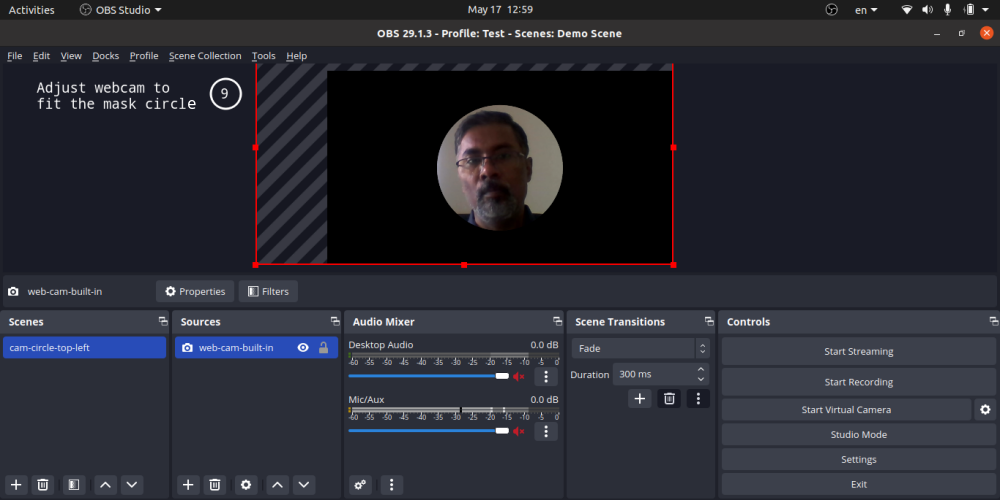
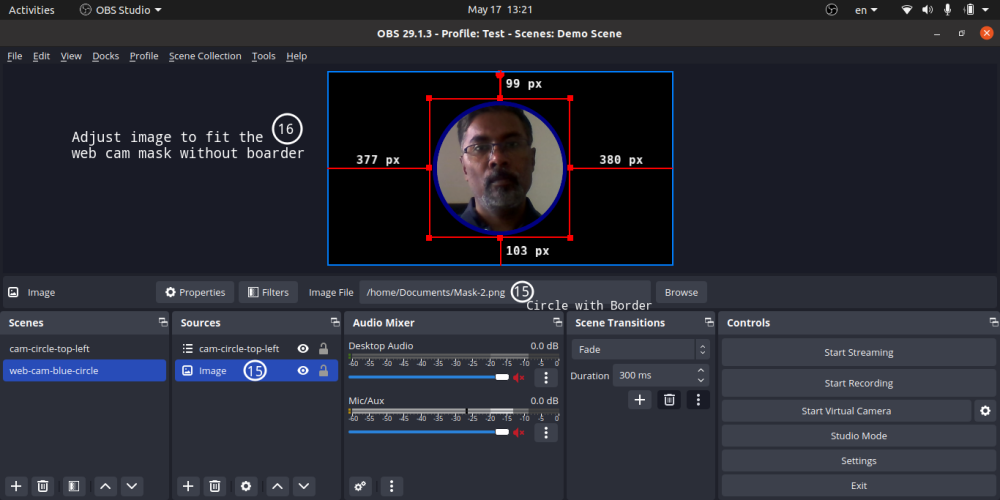
- You can add only one mask on an image or video [Right click on Scene -> Filter -> -> + -> Image Mask/Blend]
You can add image mask to your webcam using ‘Image Mask/Blend’ option as per steps mentioned here: streamshark.io/obs-guide/image-mask. The white or coloured part of the image is made transparent while applying a mask and the black pixels are made invisible. Note that the mask can be applied on the source and not one the scene. If you apply mask on a source (say web cam), any relative transform between the web cam and mask cannot be applied.
Concepts of Scene and Layers in OBS: Top layer is the visible layer.
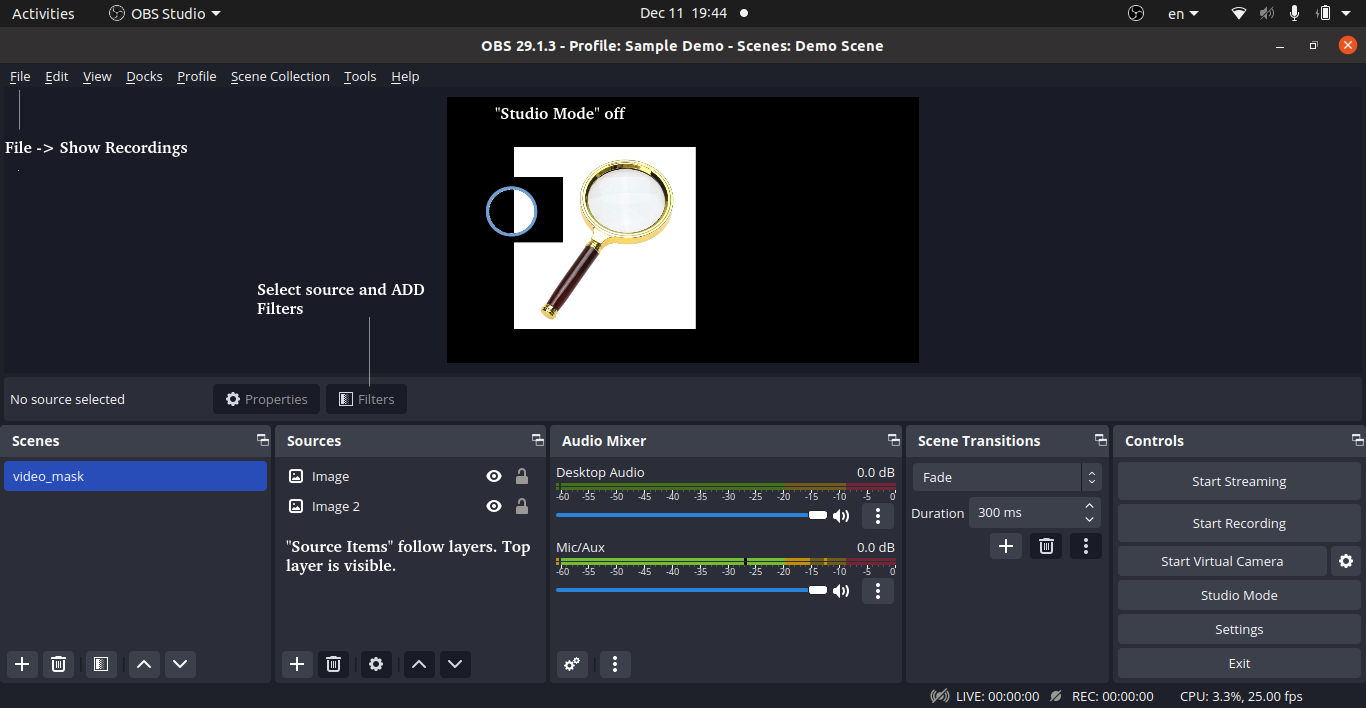
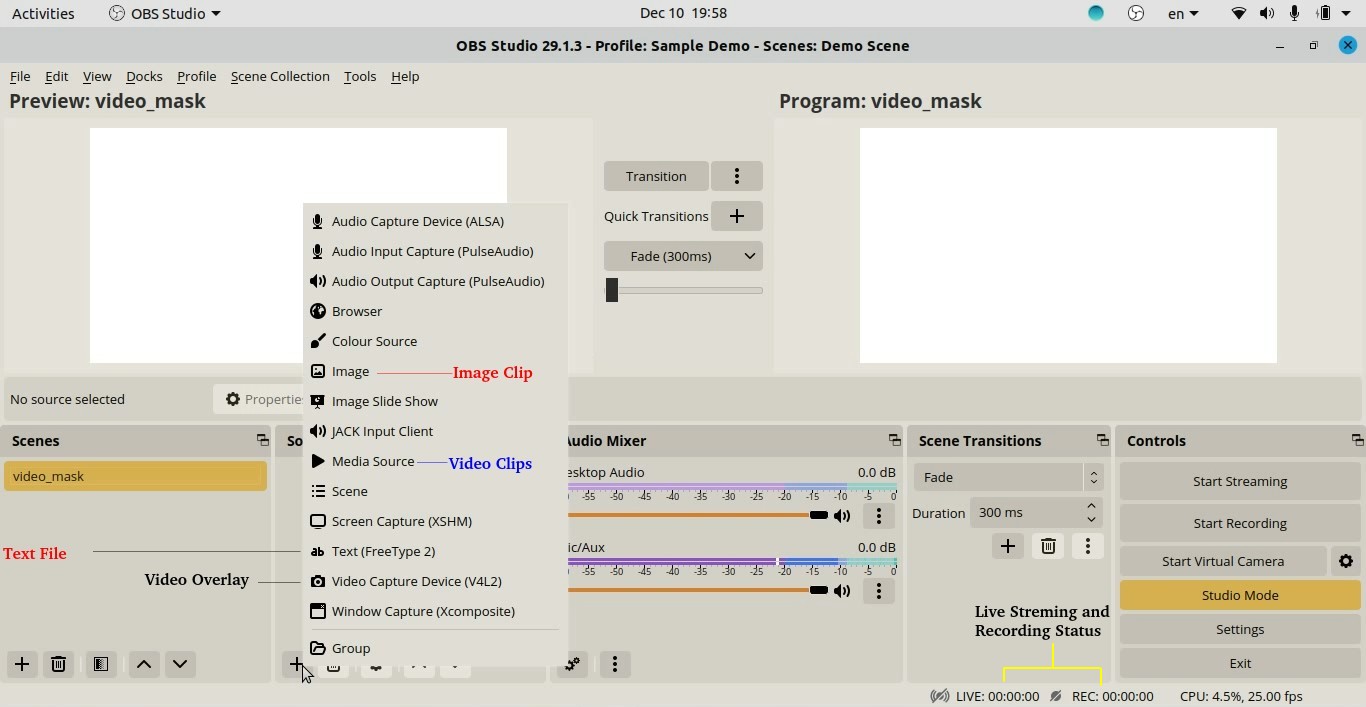
Various Types of Sources in OBS
Text Source in OBS
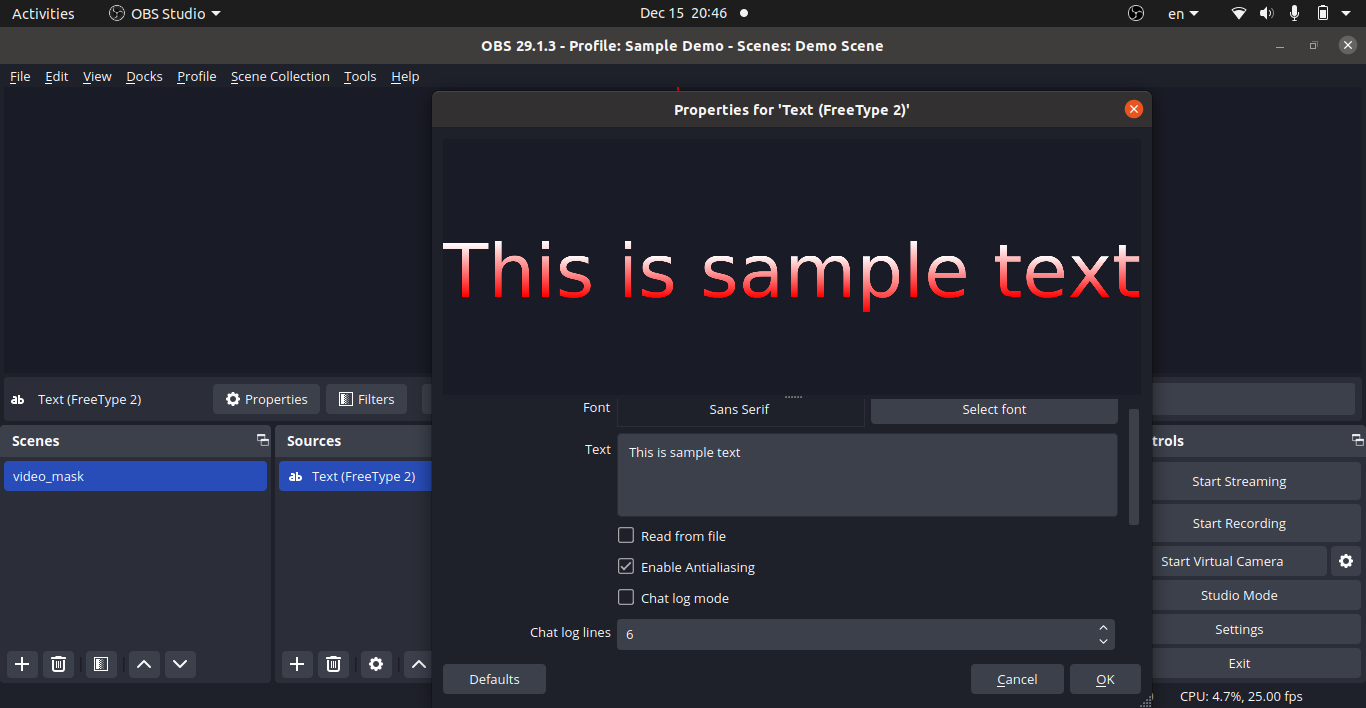
Text Source in OBS: Colour Gradient
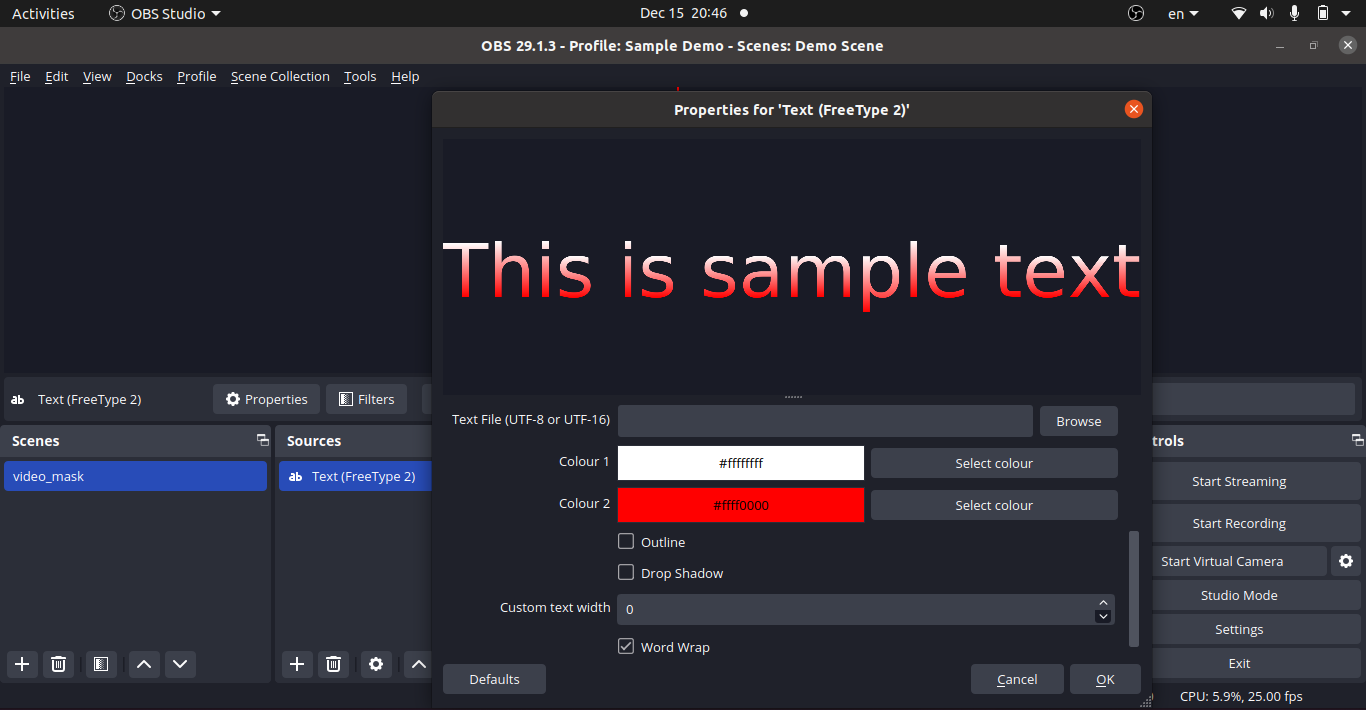
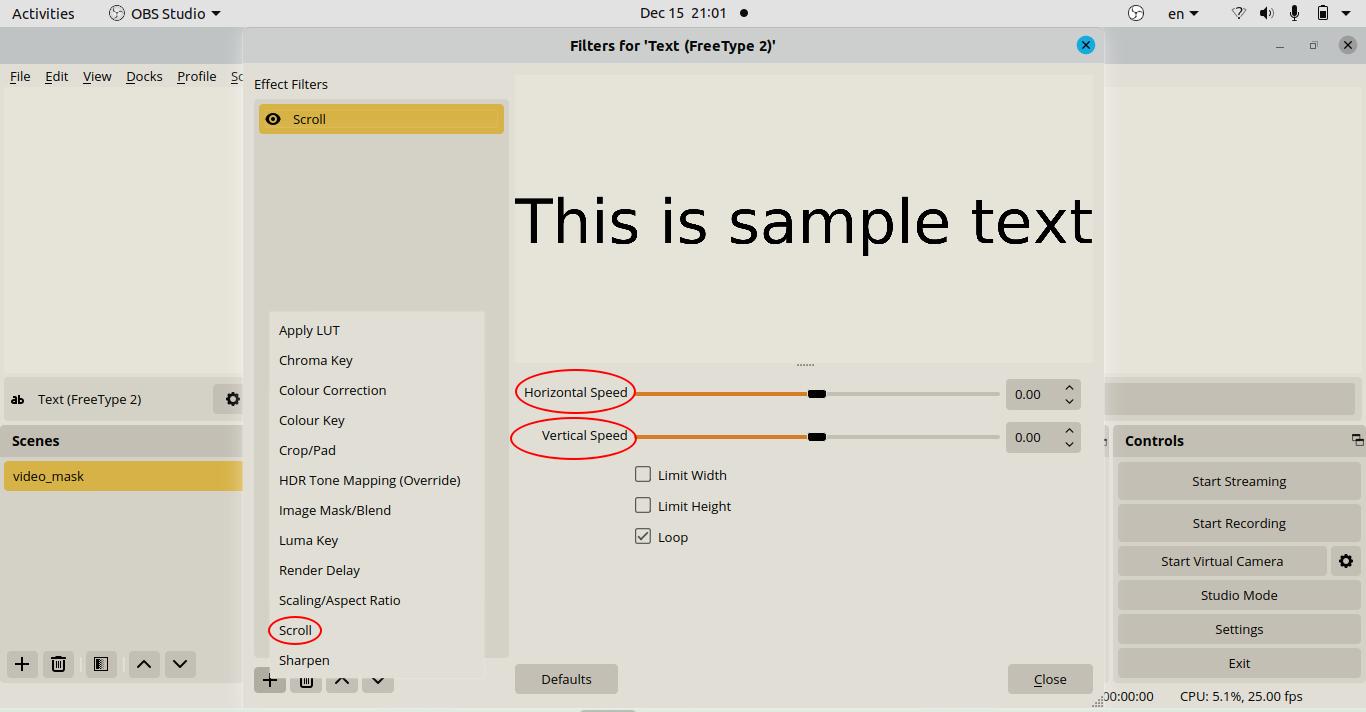
Scrolling Text in OBS
Sometimes, the recording may automatically start without you intending to do so. This is very likely due to Hotkey associated with "Start Recording" pressed during some other tasks. Following settings might rectify this issue:
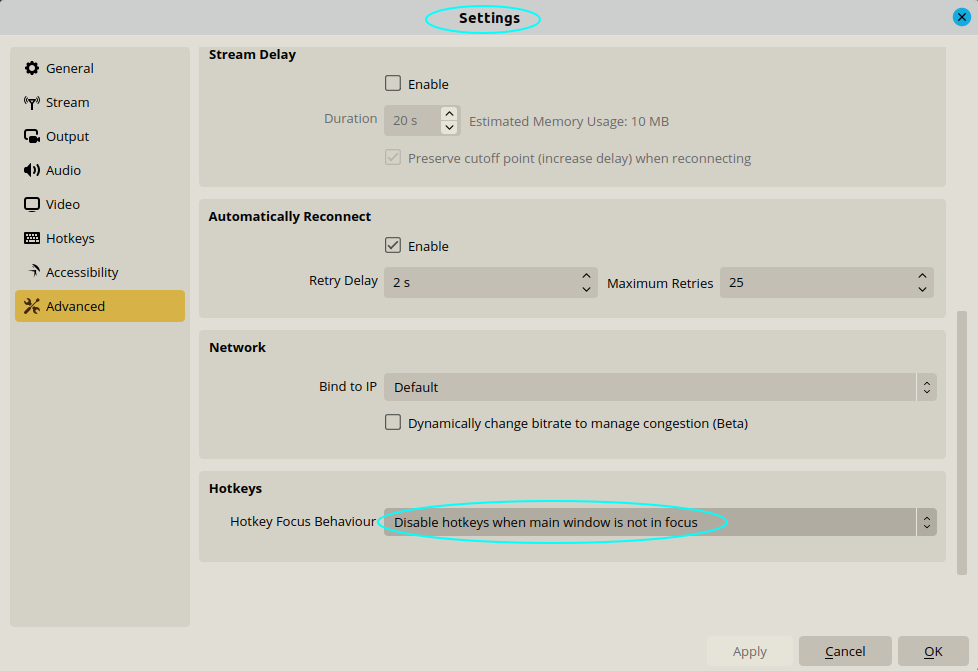
One of the drawbacks of this setting is that you cannot start OBS while it is minimized. This is specially needed when you want to capture screen (activities on the Desktop). One option is to turn on "Never disable hotkeys" before starting a screen capture, set appropriate hotkeys (keyboard shortcuts preferably with ALT key combination at ALT key is rarely used in normal keybord input of texts) for start and stop recordings. Once desired screen capture is complete, turn on "Disable hotkeys when main window is not in focus". Note that scenes and sources automatically gets added to hot-key menu. One can use combination of ^+Shift+keys on the first, second and third rows such as z, x, c or a, s, d or q, w, e for various short cuts.
During screen capturing, one may face screens which captures itself (mirror effect) as shown in following image. If available, move the OBS Studio window to a second monitor. This will prevent it from being captured in the recording. In newer versions of OBS Studio, there is option under Settings > General > check box "Hide OBS windows from screen capture".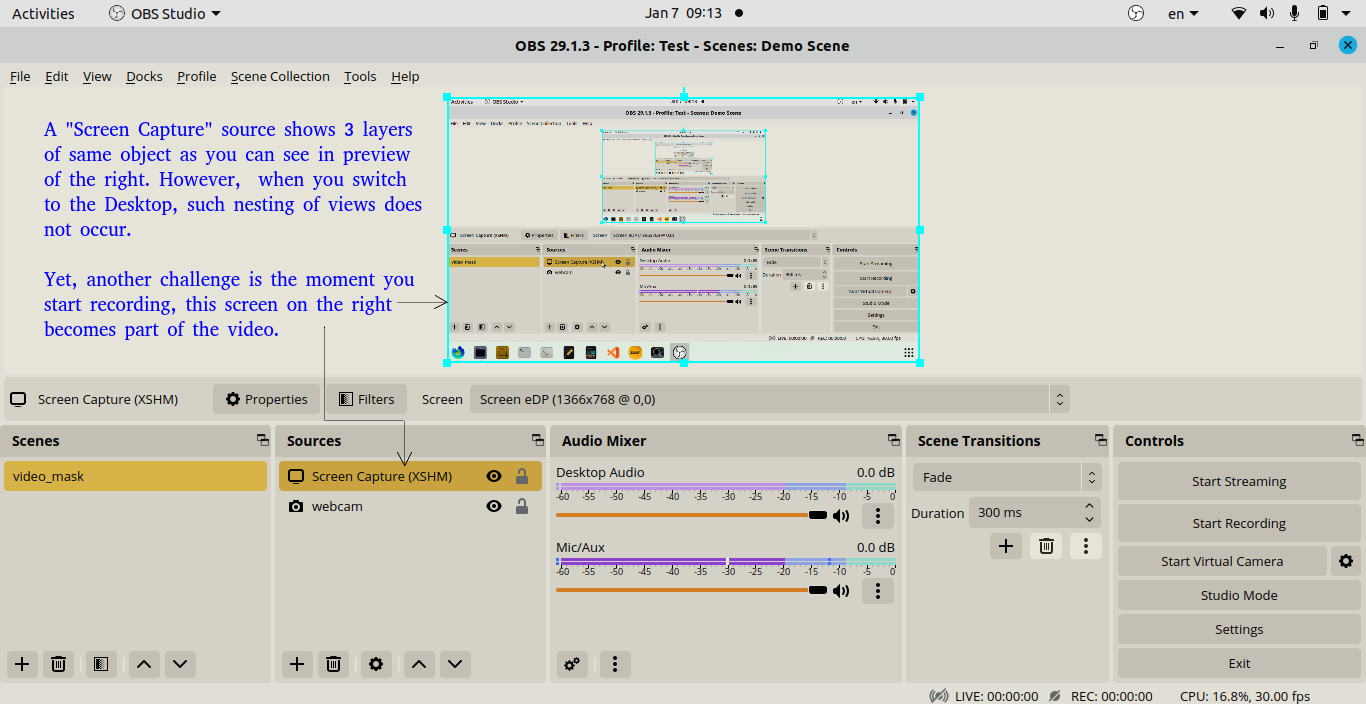
Excerpts from OBS website: "High performance real time video/audio capturing and mixing. Create scenes made up of multiple sources including window captures, images, text, browser windows, webcams, capture cards and more. Studio Mode lets you preview your scenes and sources before pushing them live. Adjust your scenes and sources or create new ones and ensure they're perfect before your viewers ever see them. Set hotkeys for nearly every sort of action, such as switching between scenes, starting/stopping streams or recordings, muting audio sources, push to talk, and more. Choose from a number of different and customizable transitions for when you switch between your scenes or add your own stinger video files."
Step-by-Step method to create a circular crop of webcam for OBS Studio. One may need to use "ffmpeg -i Image-Mask-2.png -vf colorkey=white:0.01:0.0 Image-Transparent.png" or other application to create image with white pixels as transparent. In MS-PowerPoint, one can select the shape and directly save as image where the corners of the square around the circle shall be filled with transparent pixels. ImageMagick can also be used to convert white pixels to transparent.
The content on CFDyna.com is being constantly refined and improvised with on-the-job experience, testing, and training. Examples might be simplified to improve insight into the physics and basic understanding. Linked pages, articles, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to reduce errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content.
Template by OS Templates